Imagine that you are a medical technician in an emergency room in a big city. You shuttle between the various wards, using portable diagnostic equipment to assist the medical staff to make a diagnosis. There is a lot of work pressure and there is a constant flow of patients. You simply do n’t have time to find a socket and plug your equipment. You are probably willing to put the device in a place and let it charge automatically, so that you can go to the next patient and the injured, who need fast-moving and efficient medical staff. Fortunately for you and the patient, wireless charging is already an off-the-shelf technology.
standard
Industry standard specifications are leading the development of wireless charging. The Wireless Wireless Power ConsorTIum's (WPC) standard is also called Qi (pronounced "odd"). This specification is divided into three core parts of the system-power transmitter, power receiver, and the communication protocol between the two devices. The main features of this standard are (see block diagram below):
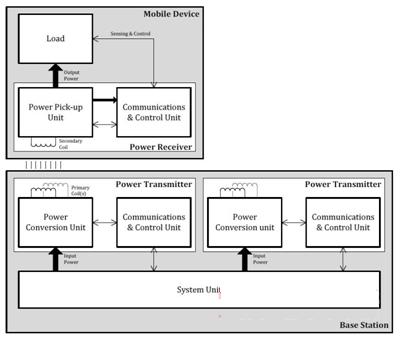
Source: Wireless Charging Alliance website
A non-contact power transmission method from the base to the portable device. The physical basis of this method is the near-field electromagnetic induction between the coils.
Use a secondary (or receiving) coil to transmit approximately 5W of power.
Operating frequency in the transmission range is 110Hz to 205kHz
There are two ways to place the portable device on the surface of the base:
1. One way is to place the portable device at a specified position on the surface of the base, and the base provides energy through one or several fixed positions on the surface.
2. Free positioning allows portable devices to be placed on the surface of the charging station at will, providing energy from anywhere on the surface.
Very low standby power consumption can be achieved, depending on the specific implementation method.
Ability to flexibly integrate the system into a portable device
A simple communication protocol enables portable devices to fully control the energy transmission process.
The energy transmission process is divided into 4 stages :
1. Selection stage: The power transmitter monitors the charging interface and detects whether the device to be charged is in place. If the device is not detected, the power transmitter will constantly ping the power receiver. If no device to be charged is detected within a given time, the power transmitter will enter standby mode.
2. Ping stage: Similar to sonar, the power transmitter sends out a digital Ping signal to detect rechargeable devices. If the device is detected, the power transmitter keeps the power signal at the level of the ping signal, and then enters the identification and configuration phase. If no device is detected, the power transmitter returns to the selection phase.
3. Identification and configuration stage: The power transmitter negotiates with the power receiver to determine how much power is provided to the device that needs to be charged on the interface. If the device is removed from the interface, the power transmitter returns to the selection phase.
4. Power transmission stage: The power transmitter provides energy to the power receiver, and adjusts the required current according to the feedback of the power receiver. When an abnormal situation occurs during the power transmission process, the safety function will turn off the power transmission in time and return to the selection stage.
This standard has been supported by more than 90 companies in various fields of the electronics industry.
technology
Wireless charging uses the principle of near-field electromagnetic induction to transfer energy from a charging pad to a portable device. At changing distances, the transmitter coil (Tx) in the charging base transmits energy to the receiver coil (Rx) embedded in a portable device such as a mobile phone. The transmitter / primary coil in the charging base generates an electromagnetic field similar to a traditional transformer when power is applied, and the induced current flows through the secondary coil on the portable device. (The charging base has a power conversion circuit that converts electrical energy into an electromagnetic field. At the receiver, the power pickup unit converts the electromagnetic field back into electrical energy to charge the device's battery). The transmitter and receiver communicate with each other to control the charging process.
Vishay Dale Electronics' IWAS series Qi wireless charging receiver coil / shield is the first commercial wireless charging coil that can be used for WPC-compliant devices. The efficiency of the IWAS series reaches 70% or higher, provides a high permeability shield for the receiving coil, blocks the charging magnetic flux, and prevents it from damaging sensitive components or batteries. The performance of IWAS series wireless charging receiver coil / shield will not be adversely affected by permanent magnets.
Stainless High Speed Blender,Baby Food High Speed Blender,Juicer High Speed Blender,Home High Speed Blender
JOYOUNG COMPANY LIMITED , https://www.globaljoyoung.com