In the beginning, the balance control strategy used by biped robots was "staTIc walking". The characteristic of this strategy is that during the robot walking process, the projection of the center of gravity (COG) is always located in the support region. The advantage of this control strategy is that the robot can stop during the walking action. Do not fall, but at the cost of very slow movements (10 seconds or more per step, because the projections that need to maintain the center of gravity are always in the support area, otherwise it will be unstable).
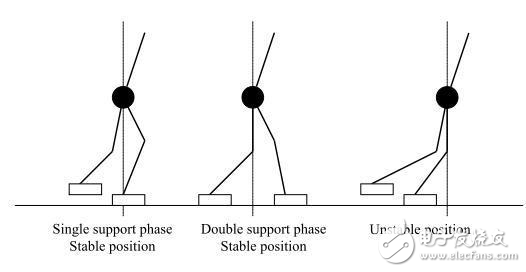
Because static walking is far from human expectations, humans have developed another walking balance strategy, "dynamic walking." In dynamic walking, the robot's speed of action is increased to no more than 1 second per step. However, the drawbacks are also obvious. It is difficult for the robot to immediately stop in the state of motion (the effect of inertia), so that the robot becomes unstable during the state transition. In order to solve the effect of inertia, a zero moment point (ZMP) has been introduced into this control strategy. In the one-legged support phase, ZMP = COG. The advantage is that when the ZMP is strictly present in the support area of ​​the robot, the robot will never fall.
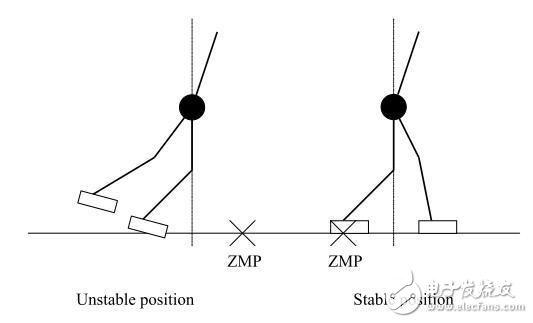
The mainstream of bipedal balance - dynamic walking based on ZMP
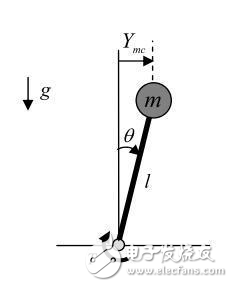
The mainstream of biped balance is now using ZMP-based dynamic walking. From the above basic content, one leg of the biped robot can be abstracted into the most basic "inverted pendulum" model in the control system.
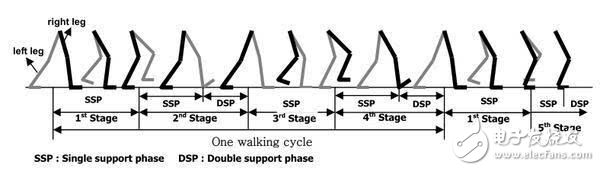
Since the bipedal balance of complex terrain cannot be achieved by a single controller, the switching strategies of multiple controllers are used to solve the balancing problem. In this strategy, the robot's walking is set to a cycle. Each cycle is divided into different stages, as shown in the following figure:
Upright Pose Controller
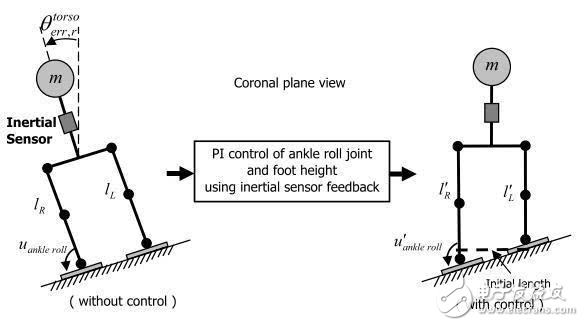
This kind of controller keeps the robot in an upright position in the sloping terrain, thus maintaining the balance of the entire body. For biped robots, the measurement of the “global tilt angle†of the sloped terrain is particularly important. A commonly used measurement method is to install a 2-axis accelerometer inside the body of the robot, and a low-pass filter to form an inclinometer.
For the pitch attitude control of the robot, the vertical attitude controller adds a PI controller with pitch error on the specified ankle trajectory:
The upright attitude controller can be implemented by the following equation:

The figure below more intuitively reflects the difference in balance control before and after using the controller:

The figure below shows the difference in balance between the roll control before and after using the controller:
Outdoor Fixed LED Display is a popular product for its high quality, every year sold to at least 80,000 pieces around the world, including Europe, North America, southeast Asia.Compared to other indoor LED display in the market, its biggest advantage is that it can display high-definition images while maintaining low power consumption.Besides, it adopts Die casting aluminum cabinet which is ultra-thin and ultra-light and owns good heat dissipation.Easy to install and maintain and suitable for multiple indoor scenes.
Application:
* Business Organizations:
Supermarket, large-scale shopping malls, star-rated hotels, travel agencies
* Financial Organizations:
Banks, insurance companies, post offices, hospital, schools
* Public Places:
Subway, airports, stations, parks, exhibition halls, stadiums, museums, commercial buildings, meeting rooms
* Entertainments:
Movie theaters, clubs, stages.
Outdoor Fixed LED Display,Led Wall Display Screen,Curved Led Display Screen,Led Display Board
Guangzhou Chengwen Photoelectric Technology co.,ltd , https://www.cwledpanel.com